Your Boss Put a Dash Cam in your Vehicle. Now what? Dealing with Driver Facing Cameras
With dash cams becoming more common in commercial and government fleet vehicles, many employees are adapting to technology that makes them uncomfortable.
In many cases, decision-makers have been so focused on procuring the right camera that they haven’t devoted enough time to getting truck drivers up and running. If you’ve been driving a commercial vehicle for a long time, you might remember similar growing pains when more trucking fleets started using GPS tracking technology.
Dash cams are at that stage in the trucking industry – relatively new technology that employees might not like all that much. But they have a tremendous upside.
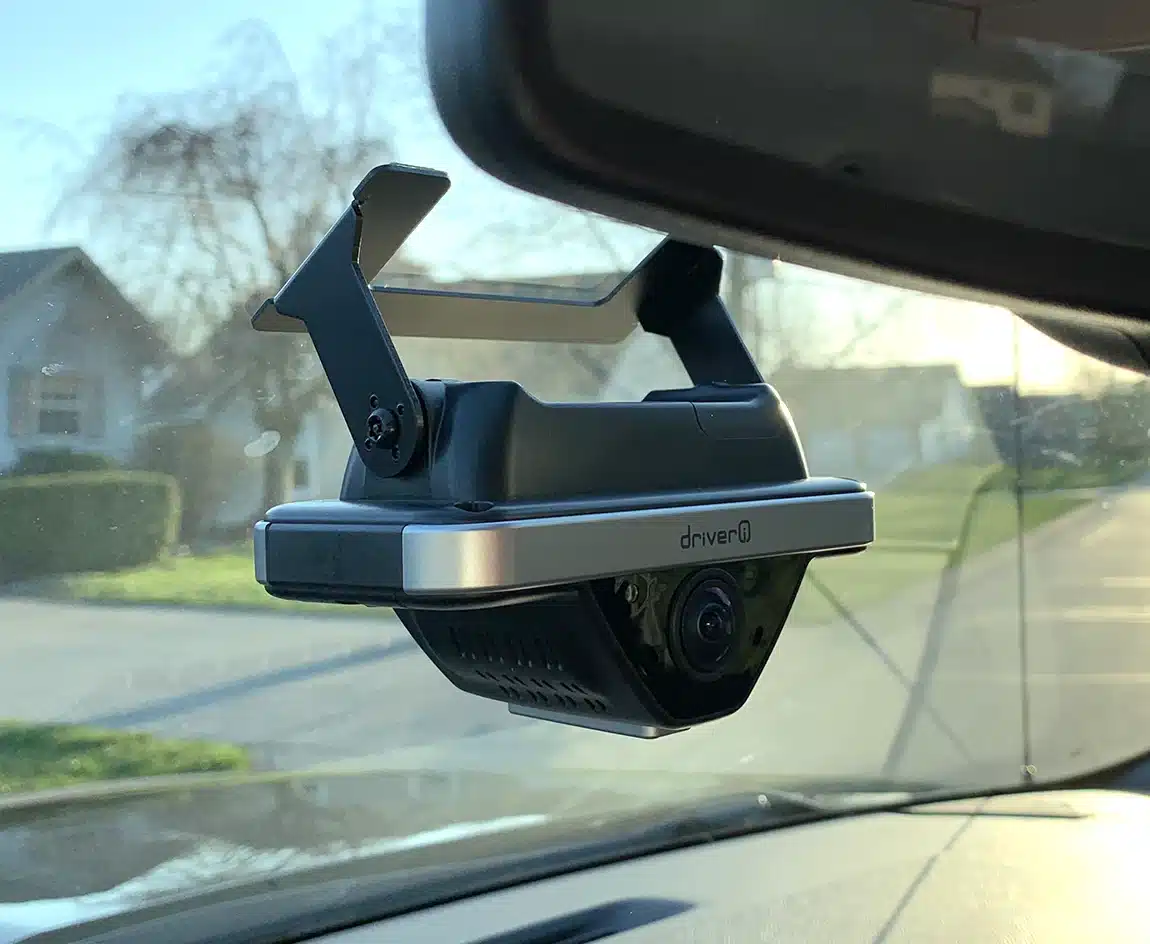
We’re here to help you, the people behind the wheel, see how to make dash cams work for you. GPS Insight’s most-popular camera is the Driveri smart camera, so most of our advice is built to take advantage of its features.
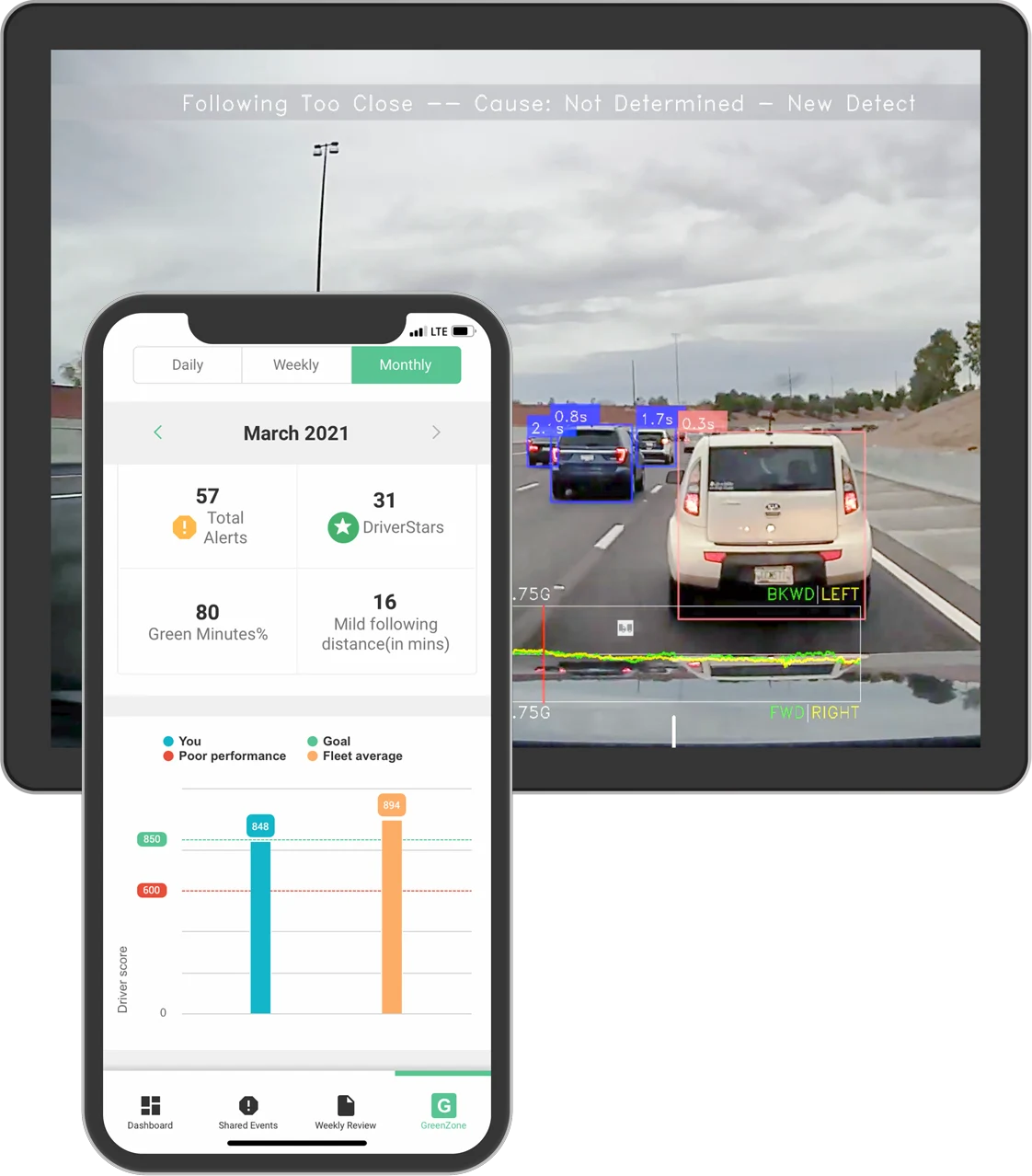
Driveri lets you coach yourself to prevent accidents from happening. By using the Driveri app, you can see where you stand so there’s complete transparency.
If your organization doesn’t use Driveri, read on – you’ll see how Driveri could do a better job of helping with driver safety compared to the camera you’re using now.
Score Big with Driveri and Trucking
Driveri is equipped with artificial intelligence that automatically analyzes what’s happening while you drive. It collects all the information it sees and gives you a score from 600 to 1,000. That’s your Driver Score.
Most dash cams are there to find fault after an accident. Driveri takes a different approach. While Driveri does capture severe and risky behaviors, it also gives you credit for safe driving. Those are your Green Minutes, which are part of your overall GreenZone score. Driveri adds to your score for safe driving actions like making a full stop at 75 stop signs in a row or making room for a vehicle parked on the shoulder of a road; that’s called a Driver Star.
Some organizations even incentive high scores. Trio Forest Products, which operates a fleet of Class 8 trucks equipped with Driveri, gives a gift card to the top driver every month.
How Alerts Work for Truck Drivers, Fleet Managers, and Trucking Companies
The AI that powers Driveri dash cams also notices unsafe driving. In many cases, you’ll get an audible in-cab warning. With speeding and following distance, if you correct yourself in time, Driveri won’t trigger an alert.
On those rare occasions when you trigger an alert, the system factors that event into your score. You and your fleet managers have the option to review the video.
Keep in mind that the Driveri camera system prioritizes the most-severe actions – speeding, following distance, traffic lights, stop signs, and distracted driving.
Key Point: Fleet Management will only see video of you if your driving triggers an alert.
The Dash Cam That Empowers You
Driveri empowers you in several ways: It lets you see where you stand in comparison to the fleet average and fleet goals; it lets you coach yourself; and it lets you contest video where the situation may not be what it seems.
Each week, Driveri will send you up to three videos showing possible areas for improvement. You’ll get them delivered automatically in your app. The system looks for trends rather than isolated events. It even calculates how many more points you’d get by improving specific recommended behaviors.
You can sign off that you’ve watched the videos so managers know you’re working on being an even safer driver.
Also, you can manually trigger Driveri to record an event. For example, if you arrive to a job and there’s a locked gate, you can trigger an alert to show why you weren’t able to access the site.
Ten Reasons to Use Dash Cameras
Since your vehicles are already equipped with telematics, why use cameras?
GPS tracking is great for efficiency and accountability information. But it leaves gaps. For example, if your GPS tracker alerts management that you stopped hard, they don’t know why. You need context.
With Driveri, you can exonerate yourself from a severe event when you are not at fault because the camera provides the context for why the event took place. For example when another driver suddenly changed lanes, and your hard stop prevented an accident.
Keep in mind: Video isn’t the point of Driveri. Managers won’t spend a lot of time looking at driver facing camera video. Instead, they’ll see charts showing safety scores at the fleet and individual levels. They’ll be able to see – without watching any video – what behaviors are most common and which ones need to be addressed.
Seeing this data in chart form is a better use of management’s time. The video’s AI capabilities make it possible to collect this data, but the video itself is secondary to the insights.
Implementing driver-facing cameras in commercial vehicles brings benefits by closely monitoring driving behavior. These inward-facing cameras, often recommended by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), offer valuable insights into driver actions and reactions, contributing to improved road safety. While there might be initial privacy concerns, the focus remains on enhancing road-facing camera systems to uphold both safety and privacy terms. Such measures align with the FMCSA’s guidelines and assist in creating a safer driving environment while respecting drivers’ privacy during appropriate times.
Benefits of driver-facing cameras in the trucking industry:
- Enhanced driver safety: Driver-facing cameras help monitor truck drivers’ behavior and attentiveness, promoting safer driving practices and reducing the risk of accidents caused by fatigue, distraction, or recklessness.
- Accident prevention: These cameras provide valuable insights into the driving habits of truckers, allowing fleet managers to identify and address risky behaviors promptly, ultimately preventing accidents before they occur.
- Distracted driving: The presence of driver-facing cameras acts as a deterrent against distracted driving, as truck drivers are aware that their actions are being monitored, reducing the temptation to use phones or engage in other distractions.
- Improved training and coaching: Trucking companies can utilize the recorded footage to offer targeted training and coaching to drivers, helping them refine their skills, make better decisions, and adhere to industry best practices.
- Real-time feedback: Driver-facing camera systems offer real-time feedback to truckers, alerting them to potential dangers such as sudden lane departures or following too closely, enabling swift corrective action.
- Litigation Protection: In case of accidents or incidents, recorded footage from driver-facing cameras can serve as valuable evidence to protect truck drivers and trucking companies from false claims or liability disputes.
- Data-driven insights: Fleet managers can analyze data collected from driver-facing cameras to gain valuable insights into driver behavior patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions about route optimization, scheduling, and overall fleet management.
- Regulatory compliance: Driver-facing cameras can assist trucking companies in complying with regulations related to hours of service, rest breaks, and other safety standards, helping avoid penalties and fines.
- Driver accountability: The presence of cameras fosters a sense of accountability among truckers, encouraging them to adhere to company policies and industry regulations, leading to a more responsible driving culture.
- Reduced insurance costs: Insurance companies may offer reduced premiums for trucking companies that employ driver-facing camera systems, as they contribute to improved driver behavior and fewer accidents.

Driveri Keeps You Safe
You might be wondering how well Driveri works. One company using this technology reduced their at-fault accidents by 83% over a year with help from Driveri.
That’s fewer drivers who have to worry about their jobs, getting medical treatment, or losing time at work.
Even more importantly, their families didn’t get a call saying that they’d been in a car accident.
Your Wingman, Not a Spy
Driveri is designed to look out FOR you, not focused on management looking IN on you.
Spying on drivers is counterproductive. It’s an ineffective use of time. Here’s what a real fleet manager using Driveri had to say:
“I don’t have the time, I’m not that interested in what you’re doing inside the cars as long as it’s safe,” said Tanner Ambs of True MHS. He manages more than 130 employees equipped with Driveri cameras.
He makes it a point to reassure new hires that he won’t see any footage of them that isn’t generated by an alert.
Wrapping It Up
To sum up, if Driveri is in your vehicle, you can put it to work for you. The Driveri app is the key to getting full transparency into your fleet’s safety program.
You’ll know where you stand in relation to your organization’s goal and your peers, as well as get the information you need to go home safe every day.
Driver-facing cameras benefit the trucking industry, truck drivers, trucking companies, and fleet managers alike. These cameras, strategically placed within vehicles, provide a comprehensive view of the driver’s actions and behavior during their journeys. Truck drivers, as the backbone of the industry, can benefit from real-time feedback and personalized coaching, leading to enhanced driving skills and safety practices. Trucking companies and fleet managers, on the other hand, gain a powerful tool for monitoring and improving driver performance, ultimately reducing accidents and improving operational efficiency.
With the data provided by driver-facing cameras, trucking companies can tailor training programs, mitigate risky behaviors, and promote a culture of responsibility among truckers. This technological innovation brings accountability, safety, and professionalism in the dynamic world of trucking.